Bezold's Abscess: Difference between revisions
Jack.Dewey (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Jack.Dewey (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
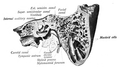
Bezold's abscess is an extension of mastoiditis into the neck space deep to the mastoid attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. | Bezold's abscess is an extension of mastoiditis into the neck space deep to the mastoid attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Sobo 1909 61.png| | Sobo 1909 61.png|Transected view of the mastoid bone. | ||
Sternocleidomastoideus.png| | Sobo 1909 58.png|Inferior view of the mastoid bone. | ||
Sternocleidomastoideus.png|Attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle to the mastoid bone. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
=== Disease Etiology === | === Disease Etiology === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
=== Patient History === | === Patient History === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
=== Physical Examination === | === Physical Examination === | ||
Patients can experience the following symptoms:<ref>Gaffney, R. J., O'Dwyer, T. P., & Maguire, A. J. (1991). Bezold's abscess. ''The Journal of Laryngology & Otology'', 105(9), 765-766.</ref> | |||
* Neck pain | |||
* Neck stiffness | |||
* Dysphagia | |||
* Otalgia | |||
* Otorrhea (in the setting of a perforated tympanic membrane) | |||
Physical exam can reveal the following findings: | |||
* Neck swelling | |||
* Auricular proptosis | |||
* Mastoid swelling | |||
* Mastoid tenderness | |||
* Fever | |||
=== Laboratory Tests === | === Laboratory Tests === | ||
Laboratory tests should primarily focus on your typical infectious workup: | |||
* CBC | |||
* CRP / ESR | |||
* Blood cultures | |||
* Gram stain and culture of otorrhea (if present) | |||
=== Imaging === | === Imaging === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
== Management == | == Management == | ||
=== Medical Management === | === Medical Management === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
=== Surgical Management === | === Surgical Management === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
== Outcomes == | == Outcomes == | ||
=== Complications === | === Complications === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
=== Prognosis === | === Prognosis === | ||
[Needs added] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 22:54, 24 November 2023
Overview
A Bezold's abscess is a complication of mastoiditis where the mastoid infection erodes through the cortical surface of the mastoid bone and forms a secondary abscess pocket near the attachment of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle.[1]
History
Bezold's abscess is named after Friedrich Bezold, a German otologist that first described it in 1881.[2]
Pathophysiology
Relevant Anatomy
Bezold's abscess is an extension of mastoiditis into the neck space deep to the mastoid attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
-
Transected view of the mastoid bone.
-
Inferior view of the mastoid bone.
-
Attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle to the mastoid bone.
Disease Etiology
[Needs added]
Diagnosis
Patient History
[Needs added]
Physical Examination
Patients can experience the following symptoms:[3]
- Neck pain
- Neck stiffness
- Dysphagia
- Otalgia
- Otorrhea (in the setting of a perforated tympanic membrane)
Physical exam can reveal the following findings:
- Neck swelling
- Auricular proptosis
- Mastoid swelling
- Mastoid tenderness
- Fever
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests should primarily focus on your typical infectious workup:
- CBC
- CRP / ESR
- Blood cultures
- Gram stain and culture of otorrhea (if present)
Imaging
[Needs added]
Management
Medical Management
[Needs added]
Surgical Management
[Needs added]
Outcomes
Complications
[Needs added]
Prognosis
[Needs added]
References
- ↑ Marioni, G., de Filippis, C., Tregnaghi, A., Marchese-Ragona, R., & Staffieri, A. (2001). Bezold's abscess in children: case report and review of the literature. International journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology, 61(2), 173-177.
- ↑ Bezold, F. (1881). Ein neuer Weg für Ausbreitung eitriger Entzündung aus den Räumen des Mittelohrs auf die Nachbarschaft und die in diesem Falle einzuschlagende Therapie. DMW-Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift, 7(28), 381-385.
- ↑ Gaffney, R. J., O'Dwyer, T. P., & Maguire, A. J. (1991). Bezold's abscess. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 105(9), 765-766.