Acute Invasive Fungal Sinusitis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jack.Dewey (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{infobox Disease |Title = |Aliases = |Image = |Caption = |ICD-9 = |ICD-10 = |MeSH = |Gene = |Locus = |OMIM = |EyeWiki = |Radiopaedia = [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/acute-invasive-fungal-sinusitis?lang=us Acute Invasive Fungal Sinusitis] }} == Overview == === History === == Pathophysiology == === Relevant Anat...") |
Jack.Dewey (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Pathophysiology == | == Pathophysiology == | ||
=== Relevant Anatomy === | === Relevant Anatomy === | ||
=== Disease Etiology === | === Disease Etiology === | ||
There are many different fungal species that can be invasive, but the most common are the Zygomycetes (''Muror'', ''Rhizopus'', and ''Rhizomucor'') and ''Aspergillus'' species. | |||
=== Histology === | === Histology === | ||
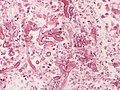
Histologic evaluation is necessary to determine the species of invasion, which can influence treatment decisions with respect to antifungal coverage. ''Mucor'' and ''Rhizopus'' are both characterized by non-septate fungal hyphae with 90-degree angle branching. Aspergillus also has non-septate hyphae, but typically has 45-degree angle branching. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Zygomycosis, mucormycosis 1.jpg|Mucormycosis | |||
Zygomycosis, mucormycosis 2.jpg|Mucormycosis | |||
Zygomycosis Mucormycosis (13430751363).jpg|Mucormycosis with intravascular invasion | |||
Aspergillosis, angioinvasive, intravascular (5390967599).jpg|Aspergillosis with intravascular invasion | |||
Aspergillosis, angioinvasive, - GMS stain (5390967417).jpg|Aspergillosis with intravascular invasion, GMS stain | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Revision as of 02:01, 23 April 2024
Overview
History
Pathophysiology
Relevant Anatomy
Disease Etiology
There are many different fungal species that can be invasive, but the most common are the Zygomycetes (Muror, Rhizopus, and Rhizomucor) and Aspergillus species.
Histology
Histologic evaluation is necessary to determine the species of invasion, which can influence treatment decisions with respect to antifungal coverage. Mucor and Rhizopus are both characterized by non-septate fungal hyphae with 90-degree angle branching. Aspergillus also has non-septate hyphae, but typically has 45-degree angle branching.
-
Mucormycosis
-
Mucormycosis
-
Mucormycosis with intravascular invasion
-
Aspergillosis with intravascular invasion
-
Aspergillosis with intravascular invasion, GMS stain